Design, Modelling and Control of an Automated TIG Welding Machine
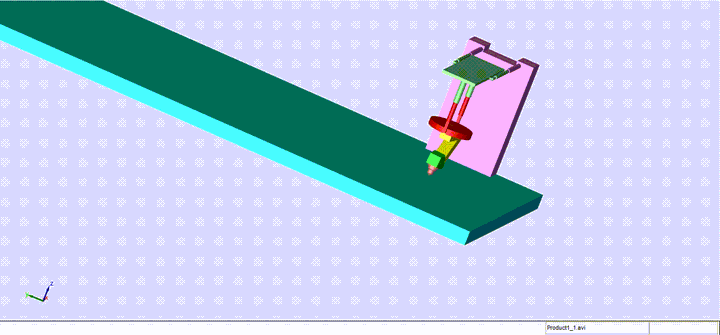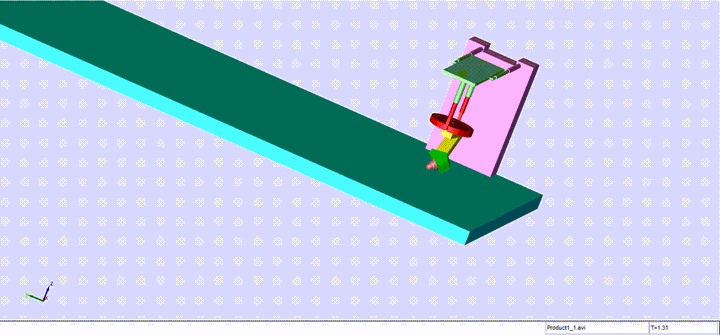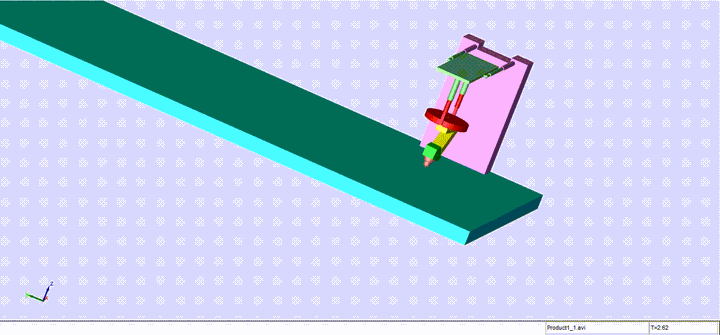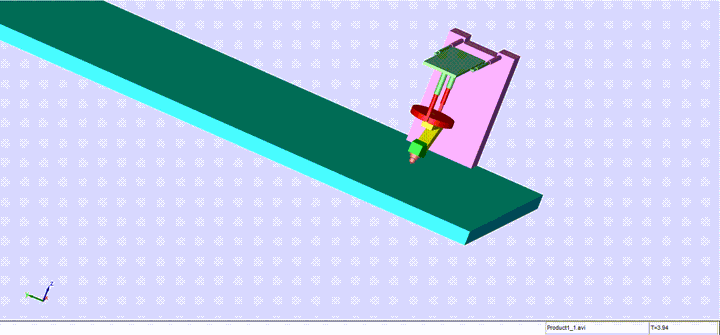
Completed design, modeling and control of a sophisticated automated TIG welding system, utilizing advanced technologies and principles. This fully automated welding machine, based on a model provided by Mitsubishi, features a robotic arm with two rotational and two translational degrees of freedom.
The machine comprises key components such as a cross slide, carriage, manipulator arms, nozzle, and bed, each playing a crucial role in the welding process. The manipulator arm, consisting of a connector arm and a rotational arm with a nozzle, enables precise control and movement during the welding operation.
The nozzle, a pivotal component, regulates the shielding gas essential for welding. Proper gas flow is crucial for preventing issues like spatter and porosity in the final weldment. The bed, acting as both a clamping platform and an electrode, facilitates the welding process by translating in the x-direction.
To control the welding process, a comprehensive machine coding system is employed. The input, provided in the form of a text file, dictates various movements and actions of the manipulator arm. Rapid traverse, linear motion, circular motion over a sphere, plane circular motion, and rotation of the welding head are among the defined actions in the code.
In addition to the physical design, the report delves into the modeling of actuation systems using Matlab Simulink. The use of PID control systems for robotic manipulators is highlighted, offering a robust and widely applicable method. The Simulink modeling includes a 3D simulation of the automatic TIG welding manipulator, allowing for the fine-tuning of key parameters such as rise time, overshoot, and settling time.
The integration of SimMechanics block library and the collaboration between SolidWorks and Matlab showcase a holistic approach to simulating and optimizing the manipulator’s motion. Overall, this comprehensive report not only details the physical components of the automated TIG welding system but also delves into the intricacies of its control and simulation methodologies.